Ischemic Stroke Detection using Machine Learning
ABSTRACT
RESEARCH QUESTION
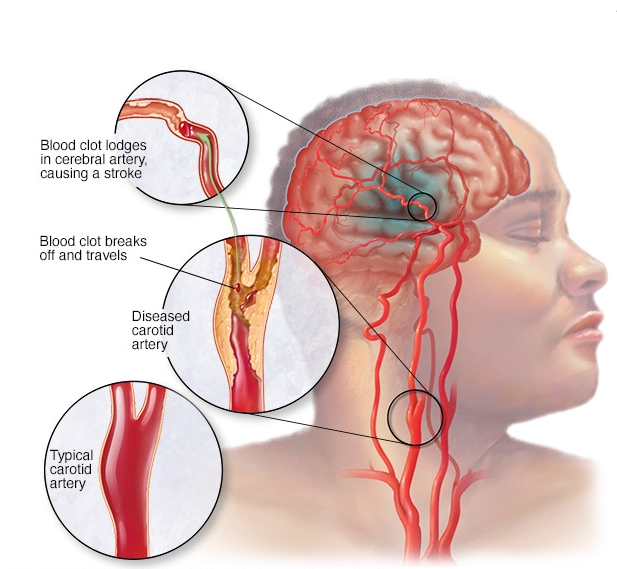
How can you create a portable, wearable product that will detect and monitor heart Strokes?
HYPOTHESIS
DESCRIPTION
METHODS
The data sets used to produce results in this presentation were taken from Kaggle. These Kaggle datasets also helped us build conclusions as demonstrated through the following figure below:
Modules
| Module | Dataset |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Module | Heart Disease Dataset |
| Stroke Detection Module | Heart Stroke Dataset |
Modeling Process
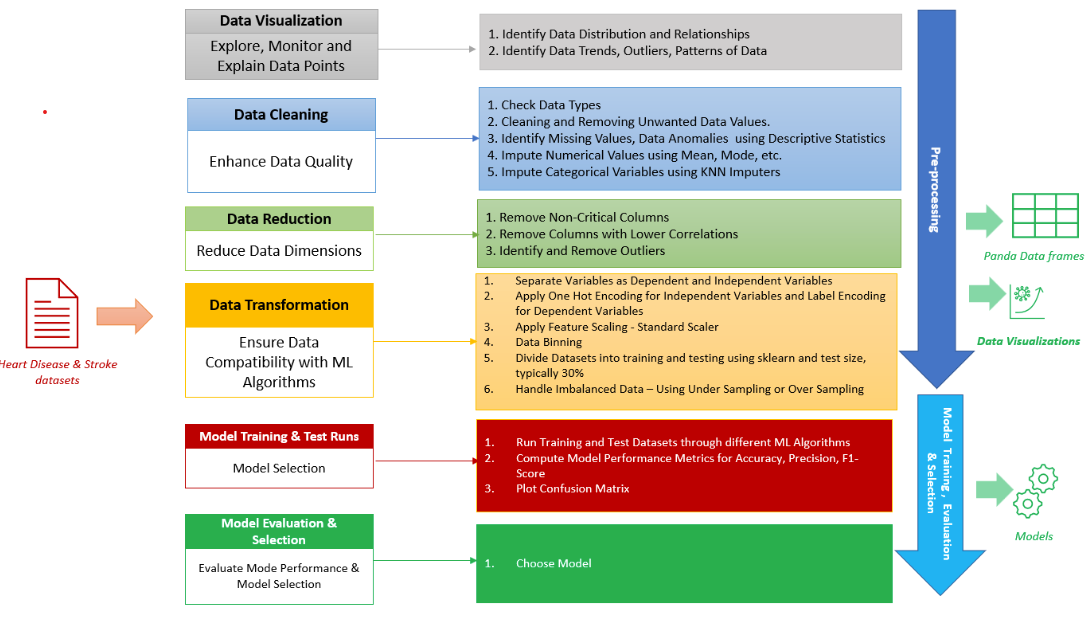
- I used the programming languages: Python and Panda - for data loading and processing, Matplotlib for data Visualization and sklearn for machine learning and statistical modeling. Also, Jupyter was used as a web-based interactive development environment for developing the models and visualization.
- Machine Learning models are a multi-step process depicted in the below figure:
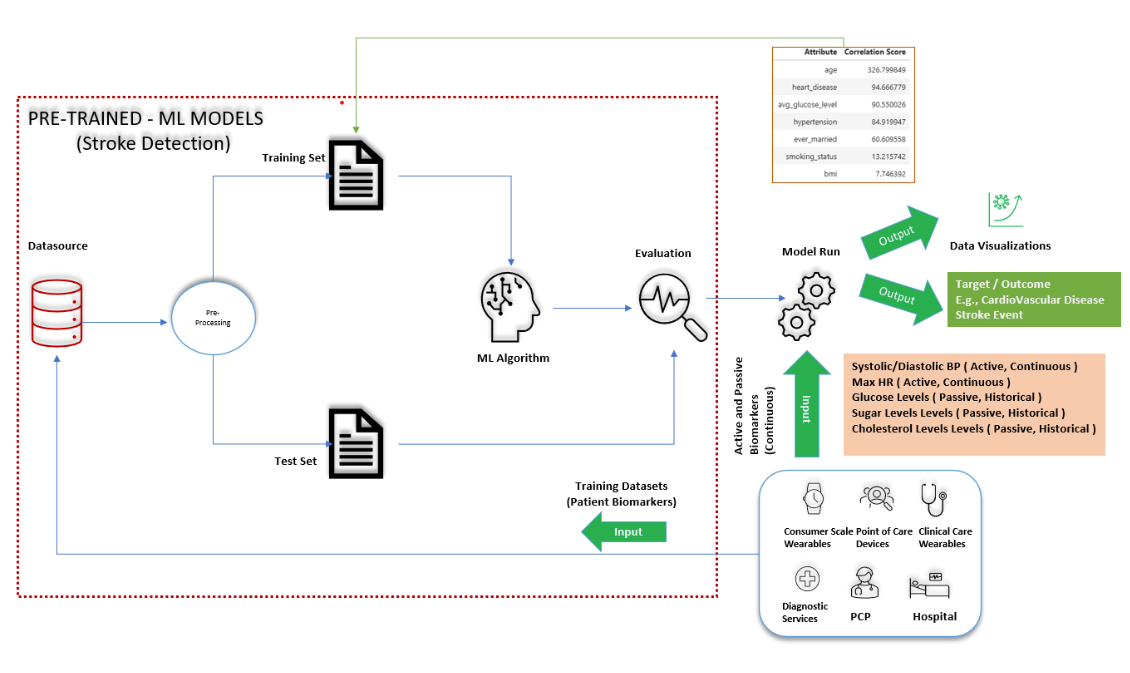
Modeling Principles
- Many machine learning algorithms fail if the dataset contains missing values.
- You may end up building a biased machine learning model, leading to incorrect results if the missing values are not handled properly.
- Missing data can lead to a lack of precision in the statistical analysis.
- Identify Data Anomalies like features having irrelevant values, like smoking status having ‘unknown’ values.
- Reduce Dimensions by eliminating dimensions that don’t contribute to the target value.
- Remove outliers data to improve accuracy of algorithm.
- Divide datasets into training and testing.
- The Independent Variables are Features that determine the Target Variable need to be at a similar scale and this specifically applies to classification algorithms. Feature Scaling is important for accuracy of distance-based algorithms like KNN, SVM etc. since they are using distances between data points.
- Handle Imbalanced Data, else you would have skewed models that will help detect target output that are biased towards the majority class of features.
- Training Datasets need to be processed via multiple algorithms for determining best performance & accuracy. Also certain models depending on the nature of datasets will be more resilient to data anomalies.
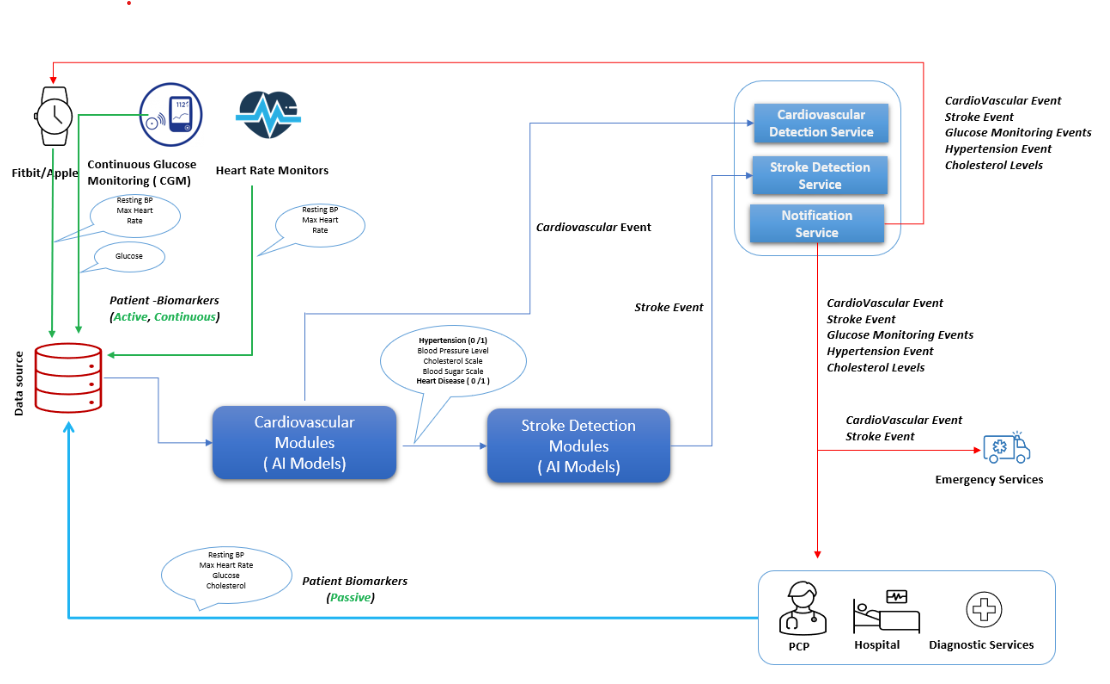
Other technologies used in the Wearable
- CGM(Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Heart Rate Monitors
- AI Models
- Cardiovascular and Stroke Detection Service
- Notification Service
Pre-processing - Data Cleaning
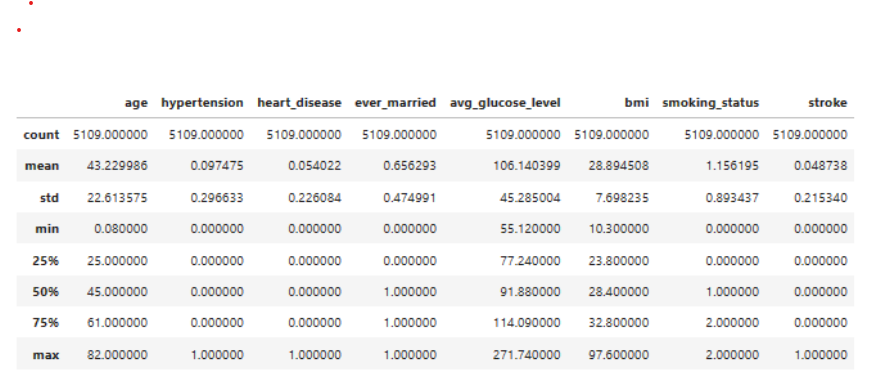
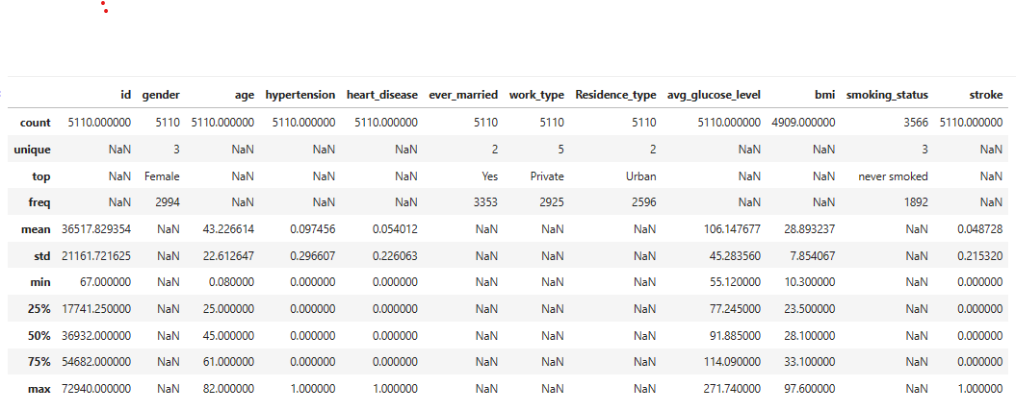
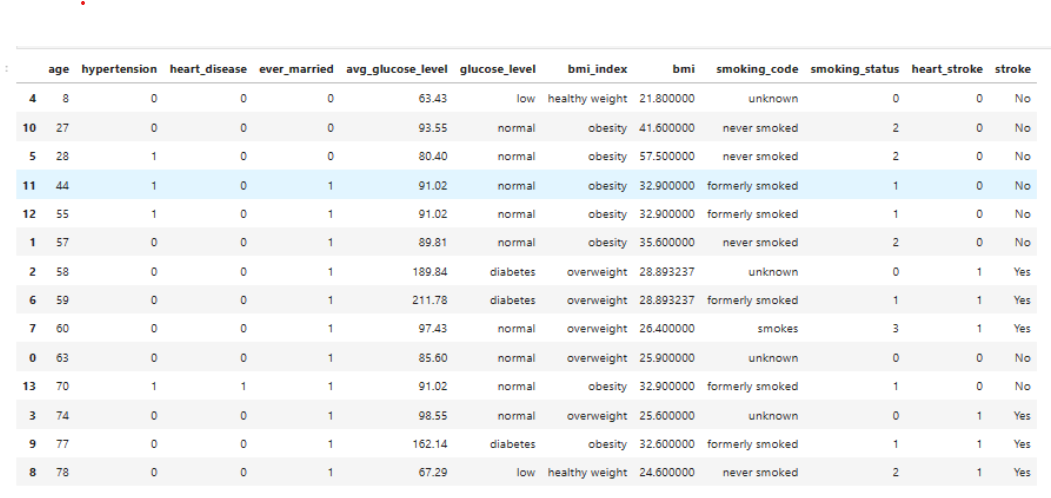
The dataset has 5110 rows. Count indicates 201 bmi null values, 1544 smoking_status with unknown values among the former smokers, never smoked, smokes. The following statistical techniques were used to address missing values & unwanted rows.
- bmi – Typically numerical variables are typically addressed by mean, forwardfill, backward fill techniques. Since 16% of missing bmi values for patients with stroke, is a large population we used mean.
- smoking_status: 30.21% of unknown values of the entire population, 18.8% of unknown values of stroke population. These values cannot be ignored. Categorical Variables are typically addressed by Univariate or Multivariate Analysis. Since there are multiple features that influence stroke occurrence as identified in the Top Correlations, I chose Multi-Variate Analysis. Out of all the techniques tested, LogisticRegression was considered best in terms of accuracy(Handling - Outlier Data as Missing Values through Imputation Methods) for 25% to 75% in the Training/Testing of Datasets.
- gender – one of the rows was labeled other, which is trivial amidst 5110 rows so it was deleted from the row in the panda Dataframe
Pre-Processing - Data Reduction
This step is meant to reduce data dimensions, increase ML Model Performance, and accuracy. The following statistical techniques were applied to the columns.
- Id – a sequence number which does not have any bearing with the Target Feature (stroke) and was removed
- Uses the following categories: age, hypertension, heart_disease, ever_married, avg_glucose_level, bmi, smoking_status
Steps- Convert the Categorical variables into Numerical variables using Label Encoding for the following categories: gender, ever_married, work_type, residence_type, smoking_status
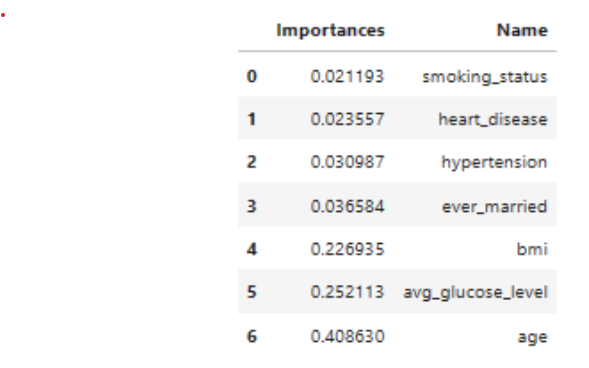
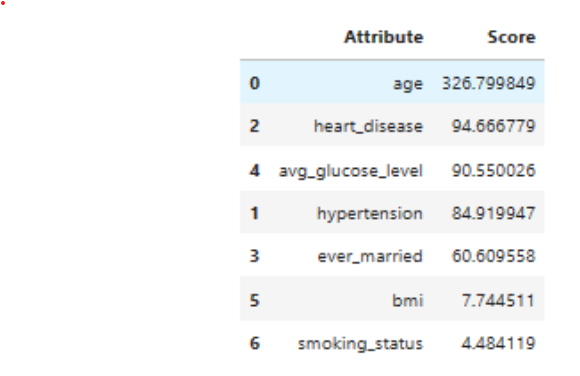
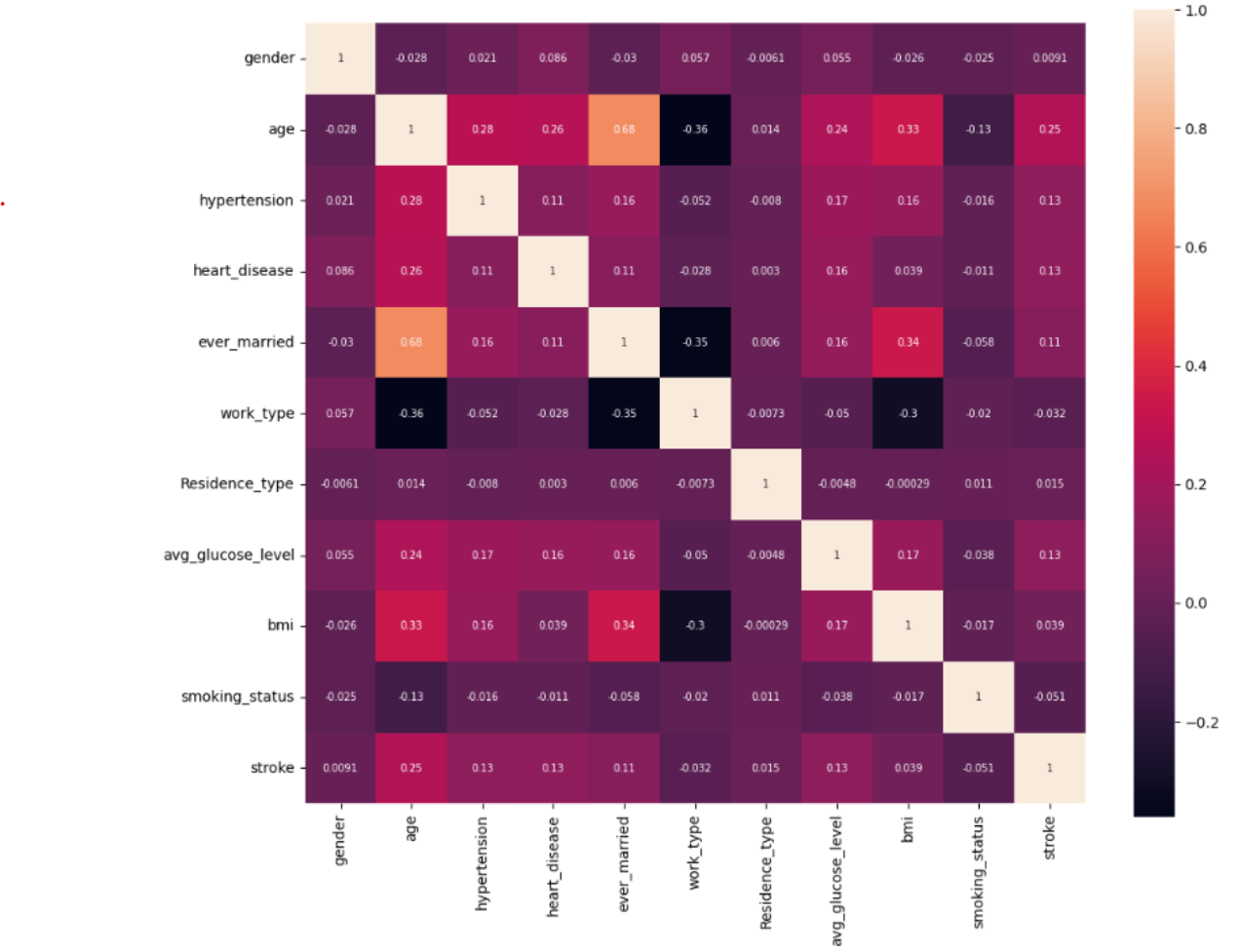
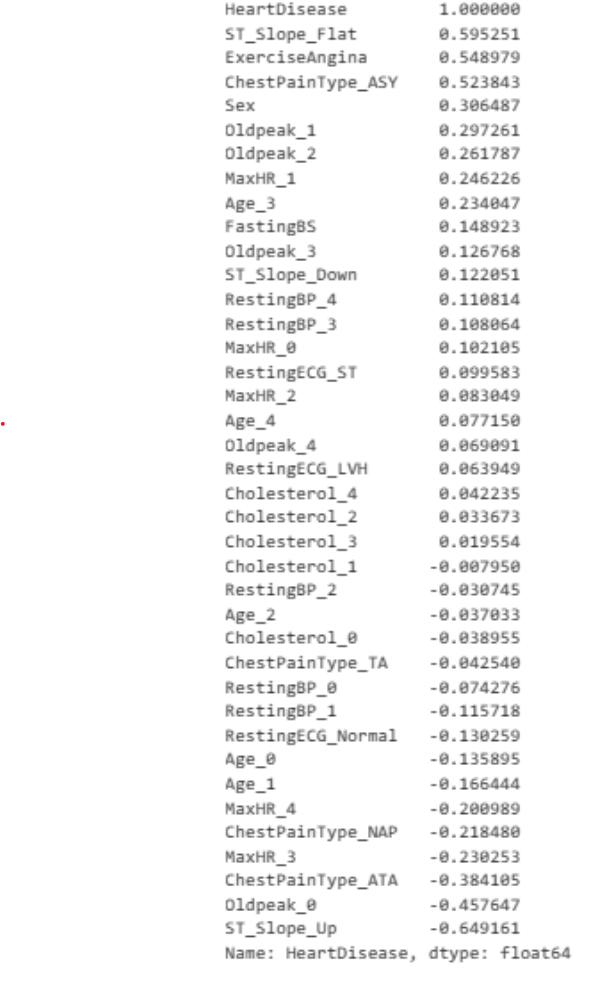
- Plotted Correlation Map – indicates a positive correlation with age, hypertension, heart_disease, average_glucose_level with the occurrence of stroke. Hence the following model attributes were removed gender, work_type_residence_type. bmi & smoking_status was one exception, needing further analysis
Pre-Processing - Data Scaling
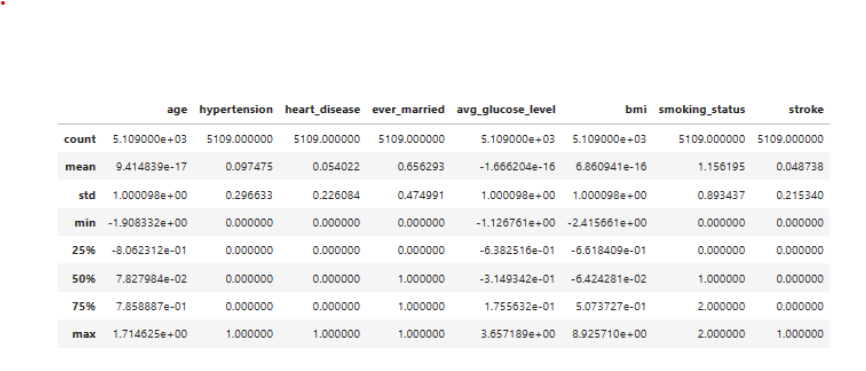
- Supervised and unsupervised learning methods make decisions according to the data sets applied to them and often the algorithms calculate the distance between the data points to make better inferences out of the data. If the values of the features are closer to each other there are chances for the algorithm to get trained well and faster. Apply feature-scaling so that the values scale into similar ranges.
- The pre-scaled data sets the standard deviation of age, avg_glucose_level, and bmi as they are significantly apart from the rest of the values. Therefore, Standard Scaling was applied to the columns
Pre-Processing - Data Transformation (Feature Engineering)
- Compute Effective Correlation to select Model Features
- Apply Encoding
- Encode all Independent Variables such as age, hypertension, heart_disease, ever_married, average glucose level, using One Hot Encoding
- Encode all Dependent Variables using the technique, LabelEncoding
- Provide Metrics for Imbalance Data. Hence, we use Smote Analysis to balance out the Training Datasets.
Pre-Processing - Data Partitioning
Split datasets into training and testing datasets. We used a 70-30% training / test dataset ratio.
Model Training & Test Runs
- Model training is the most important part of the machine learning process as it results in a working model which will eventually be validated, tested and deployed. The model’s performance during training will determine how well it will work when put into an application for the users. Both the quality of the training data and the choice of the algorithm are central to the model training phase.
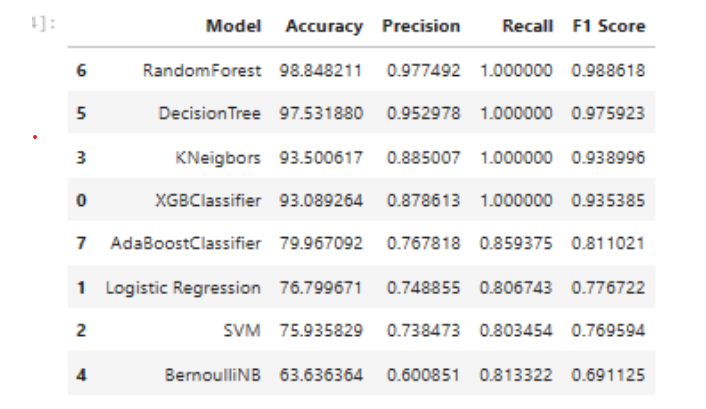
- In most cases, training data is split into two sets for training, validation, and testing. The following models were run through the same training and test datasets to evaluate Model Performance Metrics – Accuracy, Precision, F1-Score, Recall etc. Algorithms differ in accuracy and precision based on the nature of data. So, a number of models were chosen to run through the training and test datasets
- There are two types of Machine Learning Models – Classification and Regression. When the response is binary (only taking two values ex. 0:failure and 1: success) in a Machine Learning model, we use classification models like logistic regression, decision trees, random forest, XGboost, convolutional neural network etc.
Model Evaluation & Selection
- Model evaluation metrics help evaluate the model’s accuracy and measure of performance from this trained model. By using different metrics for performance evaluation, we could improve the overall predictive power of the model before production on unseen data.
- The algorithm, RandomForest has proven to have the best performance and accuracy.
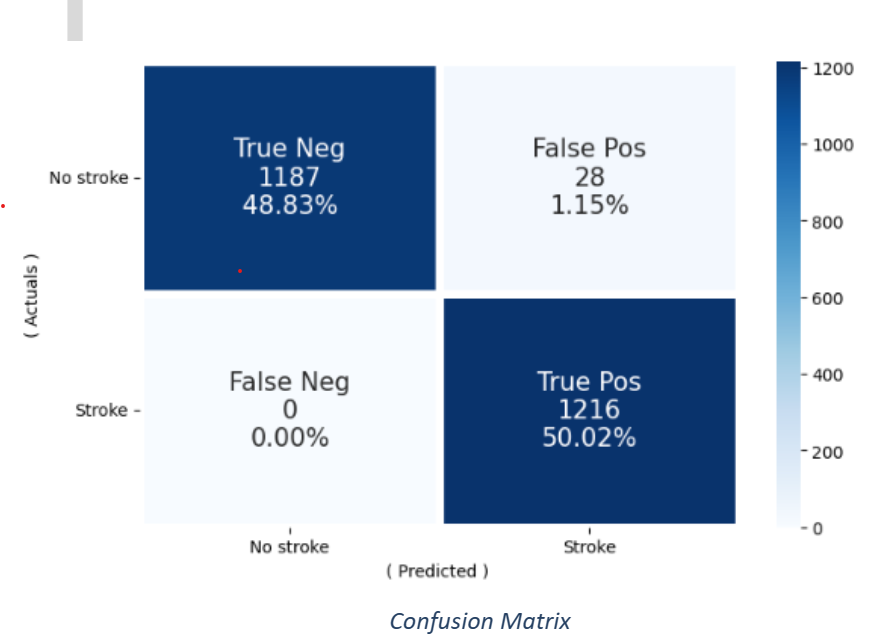
- A confusion matrix is often used to describe the performance of the classification model. This seems to be a good result considering the large number of True Positives. True Negatives are on the lower side because of imbalanced data (4860 patients with No Stroke-0, 249 rows with Stroke-1)
| What it means | Class |
|---|---|
| The predicted values (No Stroke) match the actual value, 919 times | True Positive |
| The predicted values (Stroke) match the actual value, 6 times | True Negative |
| The predicted value(No Stroke) doesn’t match the actual value (49) times | False Positive |
| The predicted value(Stroke Stroke) doesn’t match the actual value (48) times | False Negative |
RESULTS
( Cardiovascular Disease)
( Stroke Detection)